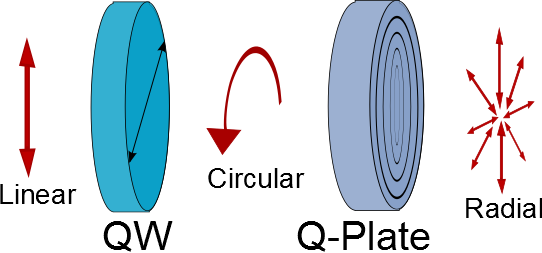
Linear entrance can be transformed in all
kinds of Polarization distributions
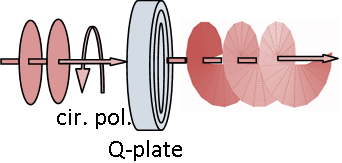
Planar wave with circular Polarization
is transformed in a helical wave
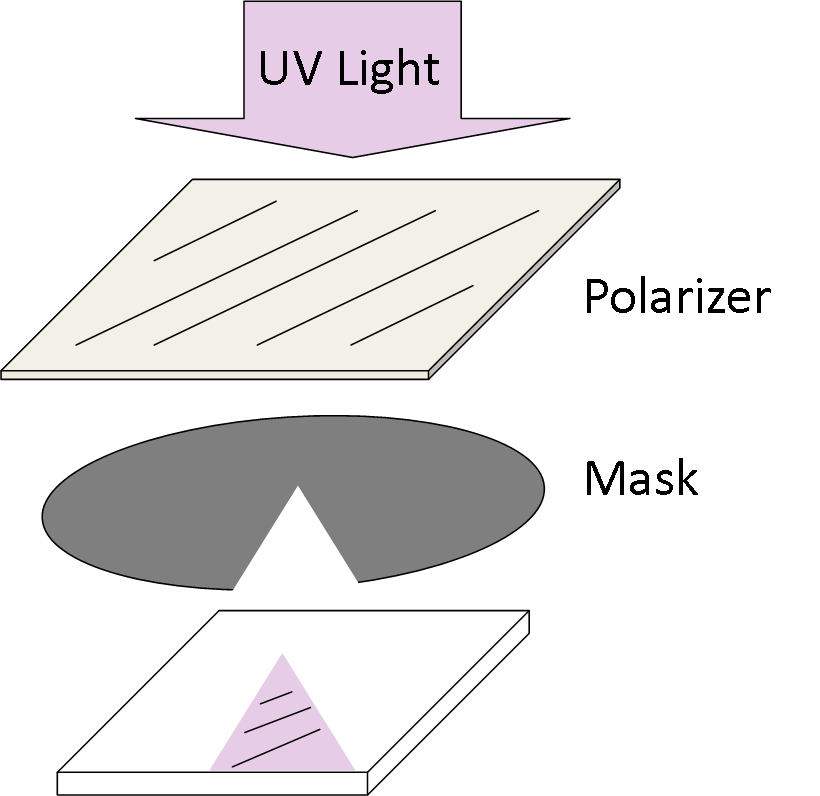
Alignment of the liquid crystal within a Spiral-plate with topological charge of 2
The variable spiral plate (VSP) is a passive liquid crystal optical element that is capable to modify a simple laser beam into a vortex beam, radial polarized beam having orital momentum (L=1 or L=2). The VSP is a perfectly transparent optical element without scattering or diffracted ligh losses (apart from the absorption losses of the material). The conversion from homogenous linear polarized beam to, for example, radial, azimuthal (or also lemon, spiral or star distribution) can simply be obtained by placing the VSP in the optical path of your laser beam. The different output Polarization patterns can be obtained by simply changing the bias applied on the Q-plate the VSP.
- Capable to generate many different circular symmetric and continuous Polarization distributions by simply changing the bias or input Polarization
- One element works for all wavelengths from 400 to 1500nm
- Works for all types of laser also femto-second pulsed lasers
- Capable to generate Orbital momentum and helical beams
- Capable to generate radial & azimuthal Polarization distribution
- No loss, no scattering, no diffraction, no segments
One interesting application of the VSP is the transformation of a planar
wavefront with circular (left or right) Polarization into a beam with an optical
vortex (with an undefined phase in the center of the beam). Such a beam carries
an orbital momentum (OAM) and has a helical wavefront as shown in the picture
below. The retardation of the Q-plate is controlled by an AC bias and can be
adjusted to any wanted value between 50-1500nm. As an additional feature, the
orbital momentum can switched on and off (within 100ms) simply by changing the
bias on the q plate.
Notice
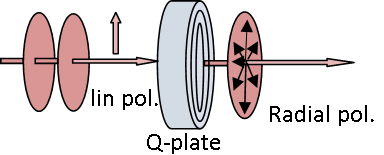
As the ARCoptix radial Polarization converter product (link), the VSP (with topology q = 0.5) is capable to transform a linear input Polarization into a radial or an azimuthal Polarization (depending of the input Polarization). The same Q-plate can be adapted to any wavelength by simply adjusting an AC voltage (0-5V) that is applied on the VSP.
The variable spiral plate can produce from a simple gaussian beam with a spiral
phase. To proove this, we create a well-known Mac-Zehnder interferometer setup
coupled to a CDD camera to record the interference pattern at the output of the
interferometer. By tilting the two beams of the interferometer, we obtain
regular interference fringes (as shown in picture) and by introducing a spiral
plate (with half wave retardation), we obtain a phase dislocation (pitchfork
hologram). Again, if the VSP retardation is tuned (via an electric bias) to full
wave retardation, the dislocation disappear as in pictures below.
An interesting recent article published in applied sciences
decribed in details the possibilities of the arcoptix S-plate.
Here is the link to the article: LINK
VSP switched off-
no disclocation

VSP switched on-
disclocation shows spiral phase
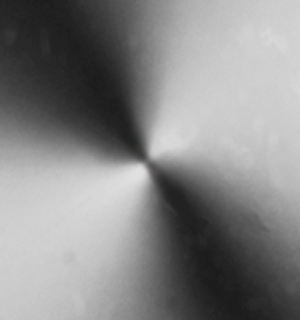
Q=0,5 (OM=1) between crossed polarizers
Radial Polarization
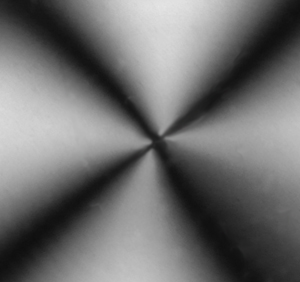
Q=1 (OM=2) between crossed polarizers
Notice that the spiral plate is similar to our radial Polarization converter
product. The principal difference between this product is that with the spiral
plate, one can obtain either a spiral or a radial Polarization and with the
Polarization converter one obtains always the radial Polarization and the spiral
phase at the same time. The differences between the spiral plate and the
ARCoptix Polarization converter are summarised in the table below.
By looking at the comparaison in the table, it seems clear that the VSP has many
advantages compared to the Polarization converter. Also, the VSP does not have
the PI phase step in the middle of the aperture, which makes the device simpler
to adjust and beam quality will be better. It is also important to note that
Polarization is a proven device that has already been used by many scientists
with full satisfaction. The VSP is a new product that does not have reference
for the moment. Notice that for optimal quality it is recommended to use a beam
size of at least 5mm in diameter. Results obtained with a beam size below 2-3 mm
may suffer from inperfection dues fundamental LC manufactring limitatios in the
center of the cell.
| Features | Polarization Converter | Variable spiral plate |
| Technology | Alignment of LC nematic with rubbing | Alignment LC nematic with polymers aligned with pol. UV light |
| Topological charge | not relevant |
Q=+/- 0.5 standard |
| Minimal Beam Size | 2 mm | 5 mm |
| Orbital Momentum | OM= +/- 1 | OM= +/- 1 on demand +/- 2 |
| Wavelength range | 400-1700nm | 400-1700nm |
| Broadband wavelength illumination | Yes possible | Max wavelength width 100nm |
| Generation of various singularities | Fix singularity | Singularity can varied with input Polarization and phase retardance |
| Radial or azimuthal Polarization | Yes | Yes |
| Spiral phase | No | Yes (with circular pol.) |
| Pi phase step | Yes need to be compensate with phase compensator | No phase step |
| Electrical driving | Yes USB LC driver recommended | Yes USB LC driver recommended |